This is a beta feature. The API documentation is currently the source of truth for evaluator configuration and behavior.
Prerequisites
You have already created prompts in the platform. Learn how to create a prompt here.Steps
Configure an LLM evaluator
Here’s a sample evaluator configuration. We’ll describe each section in detail below.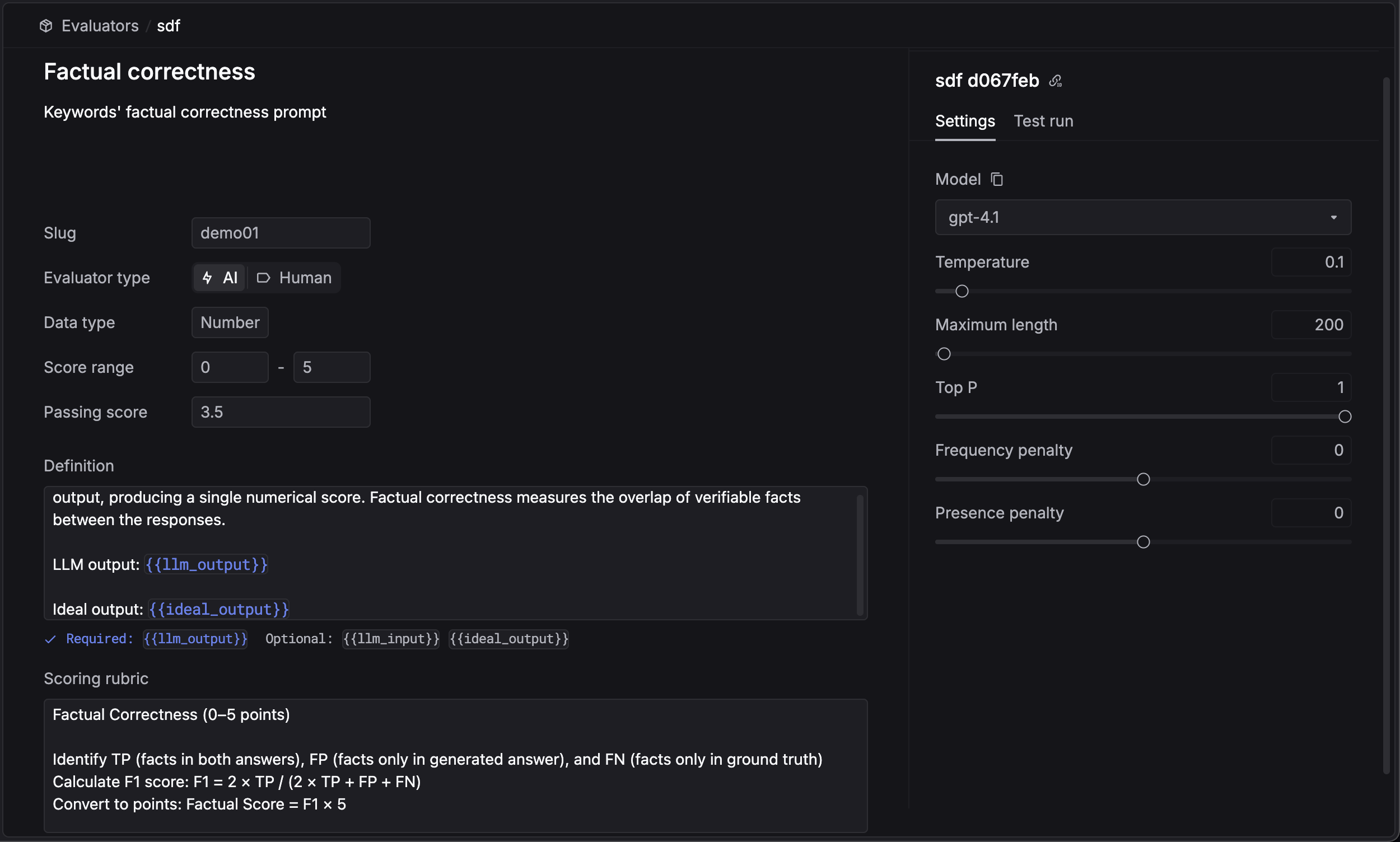 You need to define a
You need to define a 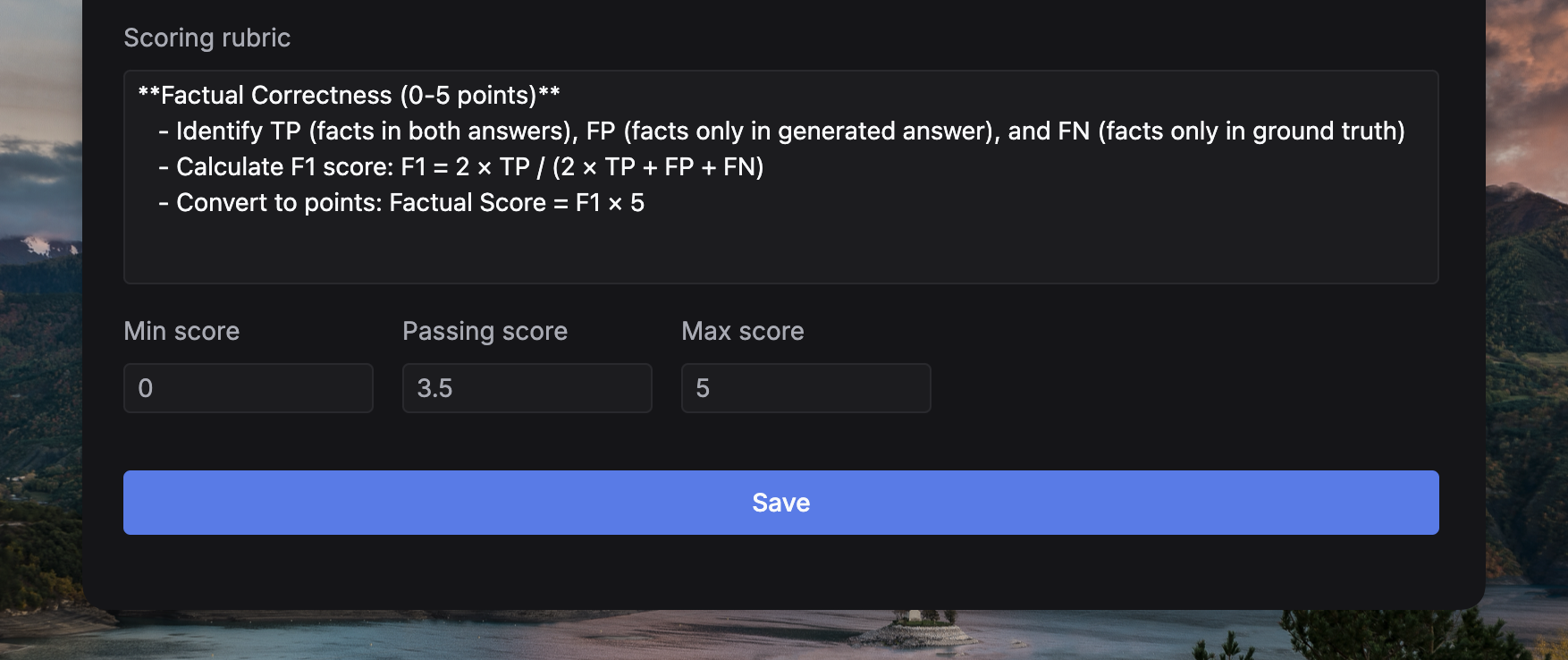 You’re good to go now! Click on the Save button to create the evaluator.
You’re good to go now! Click on the Save button to create the evaluator.

Slug for each evaluator. This slug will be used to apply the evaluator in your LLM calls, and will be used to identify the evaluator in the Logs.Then, you need to choose a model for the evaluator. The evaluator will use this model to evaluate the LLM outputs. Currently, we only support gpt-4o and gpt-4o-mini from OpenAI and Azure OpenAI.Definition (Prompt)
The definition is the core instruction for the LLM evaluator. It explains the task and expected output.You can use the following variables in your definition:{{input}}: The input prompt sent to the LLM.{{output}}: The response generated by the LLM.{{metadata}}: Custom metadata associated with the request.{{metrics}}: System-captured metrics (e.g., latency, tokens).
Ideal Output:
ideal_output is not a standalone option. If you need to compare the LLM response against a reference answer, you should include the reference in your metadata or input and refer to it in your prompt (e.g., {{metadata.ideal_output}}).Scoring Rubric
Finally, define theScoring rubric. This guides the LLM on how to assign scores based on the definition.Passing score is the minimum score that the LLM output needs to achieve to be considered as a passing response.
Understanding Unified Inputs
When an evaluator runs, it receives a unified input object containing all necessary context. This ensures consistency across different evaluator types (LLM, Human, Code).The unified input object includes:
input: The request content.output: The response content.metadata: Any custom context you provided (useful for passingideal_output).metrics: Performance data like latency and cost.